GPCR signaling
GPCR signaling
In Sept 11 there were multiple problems with the GPCR terms (Sept 11),
- 1. The GPCR terms use 'by' in their name. This doesn't seem correct as it implies that activation of AC activity is downstream of the pathway. In GO, the pathway begins with receptor-ligand binding and ends with regulation of a downstream cellular effect (normally transcription), so I think AC, PLC etc are all part of the GPCR signaling pathway. FIXED-MAY 2012
- 2. GO isn't consistent in calling them 'G-protein coupled receptor protein signaling pathway' vs 'G-protein signaling' vs 'G-protein signaling pathway'. FIXED-MAY 2012
- 3. The current is_a relationships between all the GPCR pathway terms don't convey the connection of the receptors, the G-proteins and the downstream signaling events well. FIXED-MAY 2012
In Sept 2011, the terms are of the type:
positive regulation of adenylate cyclase activity by G-protein signaling pathway ; GO:0010579 activation of adenylate cyclase activity by G-protein signaling pathway ; GO:0007189 activation of adenylate cyclase activity by adrenergic receptor signaling pathway ; GO:0071880 activation of adenylate cyclase activity by dopamine receptor signaling pathway ; GO:0007191 activation of adenylate cyclase activity by glucose-triggered G-protein signaling pathway ; GO:0010619 activation of adenylate cyclase activity by serotonin receptor signaling pathway
activation of protein kinase C activity by G-protein coupled receptor protein signaling pathway ; GO:0007205
activation of phospholipase D activity by G-protein coupled receptor protein signaling pathway ; GO:0031583
activation of phospholipase C activity by G-protein coupled receptor protein signaling pathway coupled to IP3 second messenger ; GO:0007200 activation of phospholipase C activity by adrenergic receptor signaling pathway ; GO:0071882 activation of phospholipase C activity by dopamine receptor signaling pathway ; GO:0060158 negative regulation of phospholipase C-activating dopamine receptor signaling pathway ; GO:0060162 activation of phospholipase C activity by metabotropic glutamate receptor signaling pathway ; GO:0007206 activation of phospholipase C activity by muscarinic acetylcholine receptor signaling pathway ; GO:0007207 activation of phospholipase C activity by serotonin receptor signaling pathway ; GO:0007208 activation of phospholipase C activity by tachykinin receptor signaling pathway ; GO:0007209 inhibition of phospholipase C activity involved in G-protein coupled receptor signaling ; GO:0030845
Therefore, these GPCR signaling pathway terms need to be changed to 'VIA' syntax with HAS_PART relationships, similar to other pathways. DONE One issue, is that they need to tie in with the second-messenger-mediated signaling terms:
second-messenger-mediated signaling ; GO:0019932 A series of molecular signals in which an ion or small molecule is formed or released into the cytosol, thereby helping relay the signal within the cell.
G-protein signaling, coupled to cyclic nucleotide second messenger ; GO:0007187 G-protein signaling, coupled to cAMP nucleotide second messenger ; GO:0007188 G-protein signaling, coupled to cGMP nucleotide second messenger ; GO:0007199 G-protein signaling, coupled to S1P second messenger (sphingosine kinase activating) ; GO:0001789 rhodopsin mediated G-protein signaling, coupled to IP3 second messenger ; GO:0030265
For an overview of second-messenger signaling, see Wikipedia and Figure 1 in:
[[1]]
IN SUMMARY: Binding of ligand to a GPCR, activates the Galpha protein by promoting the exchange of GTP for GDP. The active Galpha subunit dissociates from the G protein trimer (alpha-beta-gamma), and signals to a PRIMARY EFFECTOR (E.g. phospholipase C or adenylate cyclase). The PRIMARY EFFECTOR causes production or release of a SECONDARY MESSENGER (E.g cAMP, IP3, Ca++). The second messenger effects a change in a SECONDARY EFFECTOR (E.g. PKC). The route of the signal depends on the type of G protein. The main routes are:
- 1. cAMP system
- 1a Gs protein activates adenylate cyclase to promote formation of cAMP
- 1b. Gi protein inhibits adenylate cyclase to inhibit formation of cAMP
(images taken from [Wikipedia]
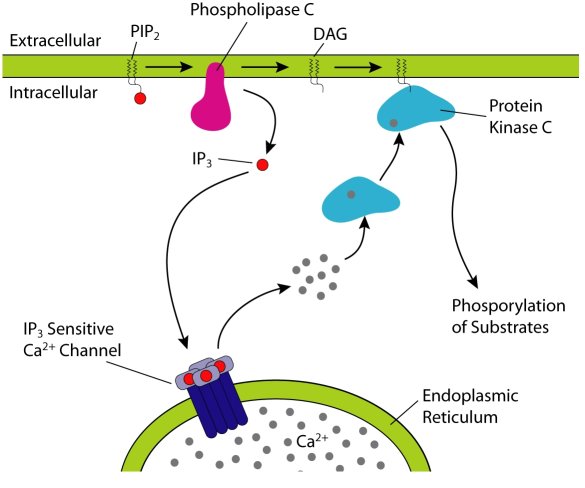
- 2. IP3 system: Gq protein activates PLC, to promote formation of IP3 and DAG. IP3 binds to receptors on the ER, which causes release of Ca++ into the cytosol. DAG reimains tethered to the plasma membrane where it recruits PKC. PKC goes on to phosphorylate a range of molecules.
Image taken from [Wikipedia]
EDITS MAY 2012
- Changed all the 'by' naming to 'via'.
E.g. activation of adenylate cyclase activity by G-protein signaling pathway ; GO:0007189 > adenylate cyclase-activating G-protein coupled receptor signaling pathway ; GO:0007189 HAS_PART: activation of adenylate cyclase activity ; GO:0007190
- Changed the is_a relationship between the GPCR signaling terms, and the second messenger terms to HAS_PART:
E.g. adenylate cyclase-modulating G-protein coupled receptor signaling pathway ; GO:0007188 HAS_PART: cAMP-mediated signaling ; GO:0019933
GPCR SourceForge Entries
- activation of PLC DONE
- intracellular GPCR TPV DONE
- opioid receptor signaling DONE
- GPCRs DONE
- GPCR transactivation DONE
Outstanding GPCR Questions
Q1. Where does 'second-messenger-mediated signaling' begin? It is under 'intracellular signal tranduction ; GO:0035556' so is limited to events within the (receiving) cell. The intracellular steps are:
- Receptor signals to activate a G protein
- G protein activates a PRIMARY EFFECTOR (PLC/AC)
- PRIMARY EFFECTOR generates a SECOND MESSENGER (cAMP, IP3)
- SECOND MESSENGER signals to a SECONDARY EFFECTOR (PKC)
- SECONDARY EFFECTOR signals to downstream proteins......
Does second-messenger signaling begin once the second messenger has been activated/released? Or does it begin upstream of this?
GPCRs
For edits to the GPCR function terms, see the receptor section of the wiki.